Anterior shoulder pain, Subacromial pain syndrome or Subacromial impingement
So in our club, some of our players came across anterior shoulder pain. Mostly it affects quarterbacks and receivers, but you can find it also in defensive backs. Our physiotherapist wrote a blog that gives you all the answers you need about this particular pain. Check it out.
Foreword Aleks Valant:
I am glad that you have decided to read the first article published on our site. Because I strongly believe in patient education, I have prepared a summary of shoulder pain or. Shoulder entrapment. The report is supported by scientific evidence and intended for anyone interested in more about a given pathology. Still, I must warn you that reading can sometimes be unfriendly to the layman, but let this not deter you from reading. I try to bring the technical language of medical research as close as possible to the average reader. Because I want to educate the reader at the highest level, all sources of knowledge and evidence are cited appropriately. I promise you that you will learn something new during the reading, and at the end of the article, you will find a quick explanation of the course of rehabilitation of this pathology.
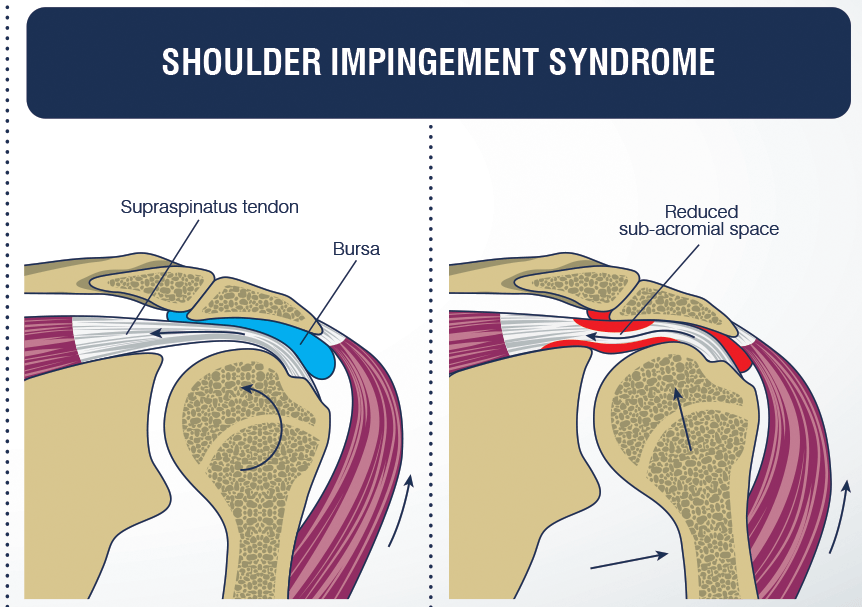
Anterior shoulder pain, known as SAPS Sub-acromial pain syndrome or SAI Sub-acromial impingement, is the most common shoulder pathology. It accounts for between 44% and 65% of all shoulder pain, and the incidence worsens with age Bhattacharyya, Edwards, & Wallace, 2014.
It is distinguished from other diagnoses and pain conditions according to the established diagnostic criteria. Patients complain of pain while raising the arm to the side, working above head height, and lying on the affected side. It mainly occurs for no real traumatic reason and slowly worsens. Patients also notice a decrease in internal shoulder rotation, which, however, in most cases does not preclude daily activities Urwin et al., 1998.
Why it occurs and how it happens is currently unknown. The presumed mechanism of formation is a combination of the effects of joint structure, imbalance of shoulder and scapular muscles, shapes of bone structures and biochemical responses of the body e.g. inflammatory changes. However, it is common knowledge that pain is caused by a reduction in the space between the tendon m. supraspinatus and an acromion - a bony outgrowth of the shoulder irritates - and squeezes the tendon while sliding during the execution of the movement Bjornsson, 2012.
A combination of anamnesis and a set of 4 tests are used to make the diagnosis, which is currently proven to be the gold standard of diagnostics without diagnostic imaging; ultrasound, MRI. However, the diagnosis does not end here, as these tests only tell us which diagnosis is present, not its cause. In addition to the use of tests, it is necessary to assess the movement of the shoulder and shoulder complex, the direction of the thoracic spine, connective tissue deprivation, and the strength of individual shoulder and shoulder muscles Park et al., 2005.
Once diagnosed, we opt for conservative treatment or physiotherapy in most cases, as evidence suggests that surgery does not offer better outcomes but brings additional adverse complications Diercks et al., 2014. In severe cases, in addition to physiotherapy, the application of an injection into the joint is also indicated, which only serves to help alleviate the problems at the beginning of rehabilitation. Injections into the joint are usually performed by interventional radiologists, as ultrasound-guided injections are more accurate than blind ones and lead to better treatment outcomes Akgun, Birtane, & Akarimak, 2004.
As already stated, there is strong evidence that physiotherapy rehabilitation effectively reduces shoulder pain and improves shoulder function. The physiotherapeutic treatment of SAPS consists of several modalities determined on an individual basis, as the patients are not the same. Current evidence supports using a combination of therapeutic modalities from the following selection: stability and strength exercises, mobility exercises, manual therapy, capsular stretching, electrical stimulation of the muscles, and shock wave therapy ESWT Tate et al., 2010.
Rehabilitation course:
Immediately after the diagnosis and a thorough examination of the condition, we start with the right therapy. The first therapy is intended to relieve pain and soothe the resulting situation. For this purpose, passive modalities of manual therapy, electrostimulation, cooling and mobilization exercises are primarily used. Light activities are started during the first therapy, intended to alleviate the initial condition and is individualized according to your situation. You continue to perform lighter exercises at home, thus trying to stop the return to the original state. Followed by 2-3 therapies, where activities are gradually added, and supportive modalities are performed. These therapies are performed at intervals of 1 or 2 weeks, as the condition needs to be calmed after intensive treatment. At the same time, therapeutic exercises show their actual effect after 2-3 weeks.
The estimated length of the entire rehabilitation is at 6-8 weeks for athletes, 12-16 weeks, as they require more from their bodies. 4 to 6 therapies are usually prescribed during this rehabilitation period. Still, the exact number cannot be predicted, as there are currently only framework rehabilitation protocols. The vast majority of SAPS resolves without additional treatment; surgical treatment is indicated only in rare cases.

